The art of the field study
To understand the full richness and variety of what people do when they are using Google, we spend many hours in the field, watching people search and listening to what they say as they do this. We hear it when they're happy, and when they're terribly frustrated. And perhaps most importantly, we also pay attention to the things they don't say -- the inexpressible "gotchas" that slow users down or get in the way of their search.
It turns out that people are masters of saying one thing and doing another, particularly when it comes to nearly automatic behavior. We find that searchers often turn so quickly to Google that they don't really think too much about what they're actually searching for. It's surprising, but often we'll see people trying to find out something about a topic, but then never actually mention the topic itself. That is, there's often a big discrepancy between what they'll tell me (the human observer) they're trying to do, and the search terms they enter into Google. One person I shadowed for the day spent ten minutes trying to find the schedule of the ferry that runs between San Francisco and Larkspur, but somehow only thought of adding the word "ferry" much later in their search.
We also study eye tracking. The eye makes a complex scan path over the search results, building up a composite picture of what is presented on the page. It's clear that what actually happens is a very rapid scan and assessment of each result as they are seen. In those milliseconds between the eye landing on the first fixation and seeing a few results, all kinds of decisions and choices are made--nearly all of them subconsciously.
In this short video, you can see three different searchers all looking for the same thing (in this case, a child's backpack). The red dot is the searcher's gaze moving around on the search results page. Notice how methodically the gaze moves from result title to title, occasionally inspecting the snippet text to gain more detail about the result.
(Video courtesy of Kerry Rodden)
So the job of figuring out what people actually do when they search isn't as simple as asking someone what they search for during the day. It's basically impossible to give an accurate telling of what you saw (or didn't see) on the results page while actively searching for a high quality results.
Memories of your own behavior are also notoriously unreliable. People's search behavior in the lab is often different than when they're at home or at work. This is a natural (and expected) side effect of lab studies: people will work especially hard to please a researcher. If we ask them to search for a pair of brown shoes they'd like to buy for themselves, in the lab they'll find the first pair that seems reasonable and then stop, satisfied. If it was real, they would go on and spend more time. We still do lab studies, but we know what to watch for, and what to ignore.
Data from field studies gives us insight into how people respond to the Google experience in ways that we can't otherwise measure.
For instance, in several field studies we discovered that many of the people who went to the previous version of the Advanced Search page had a strong, almost visceral negative reaction when the page appeared. The text of the original page had language that many people saw as intimidating--words like "Domain," "Usage Rights" and "Safe Search" can be a bit much if you're not sure what they mean.
The old Advanced Search page was a little off-putting (click on the image to see a larger version):
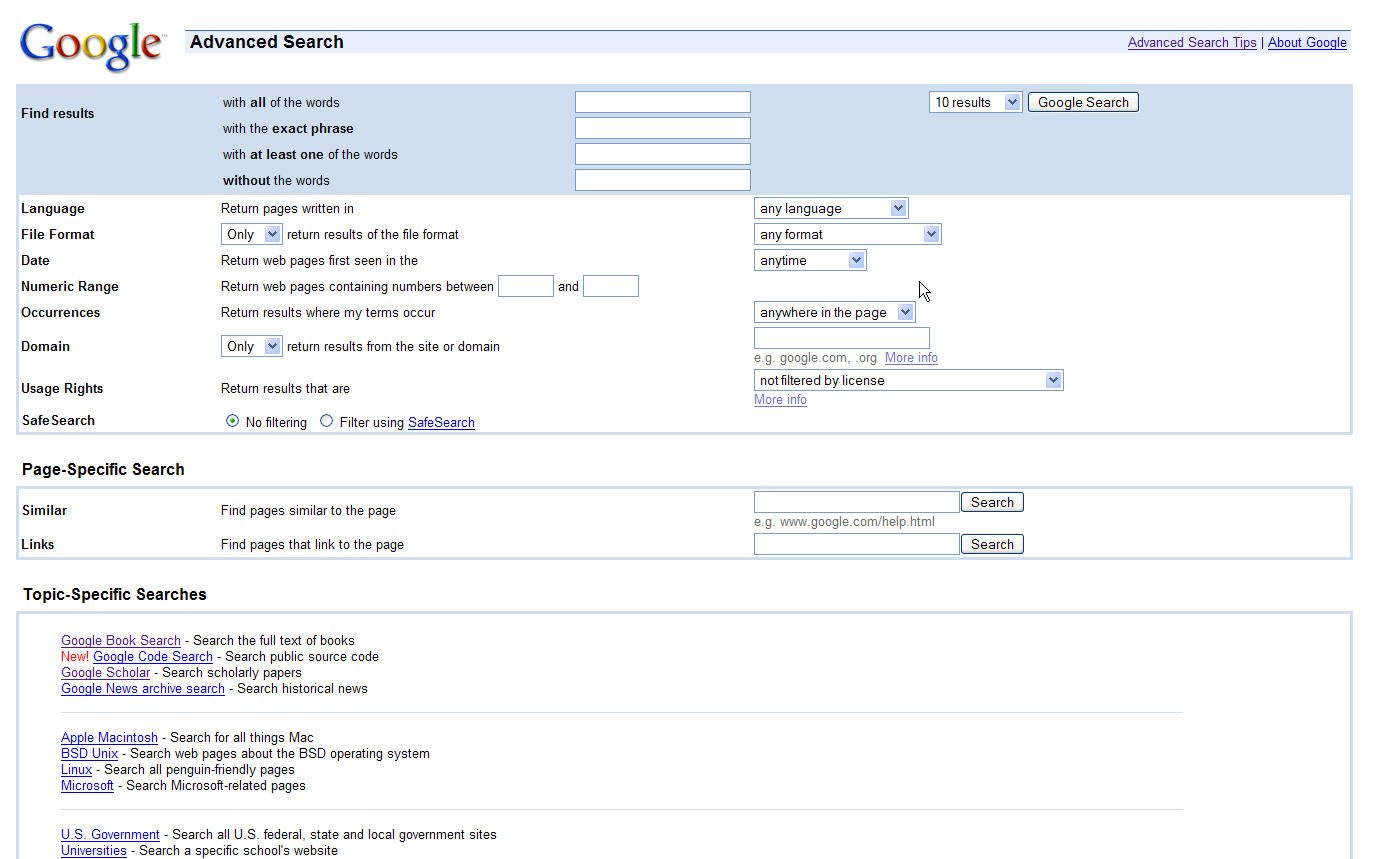
Based on our field studies, we dug more deeply into how people were actually using our Advanced Search page, and quickly discovered that, indeed, a large number of users were going to the page, and then leaving it without ever filling in any of the slots.
Armed with this insight from field studies, we redesigned the page, simplifying it by removing terms that were unclear to the average user (the word "occurrences," for example, just didn't mean anything to many of the Advanced Search page users), moving rarely used features (numeric range searches, date searches, etc.) into a part of the page that was expandable with a single click. That made them easy to get to for people who knew they wanted to search with those restrictions, but out of the way in a non-threatening way.
One of the other things we noted in the field study was that people often didn't understand how the Advanced Search page worked. So we added a "visible query builder" region at the top of the page. As you fill in the blanks, the box at the top of the page fills in with the query that you could type into Google. It was our way of making visible the effects of advanced search operators.
The Advanced Search page post-redesign (click on the image to see a larger version):
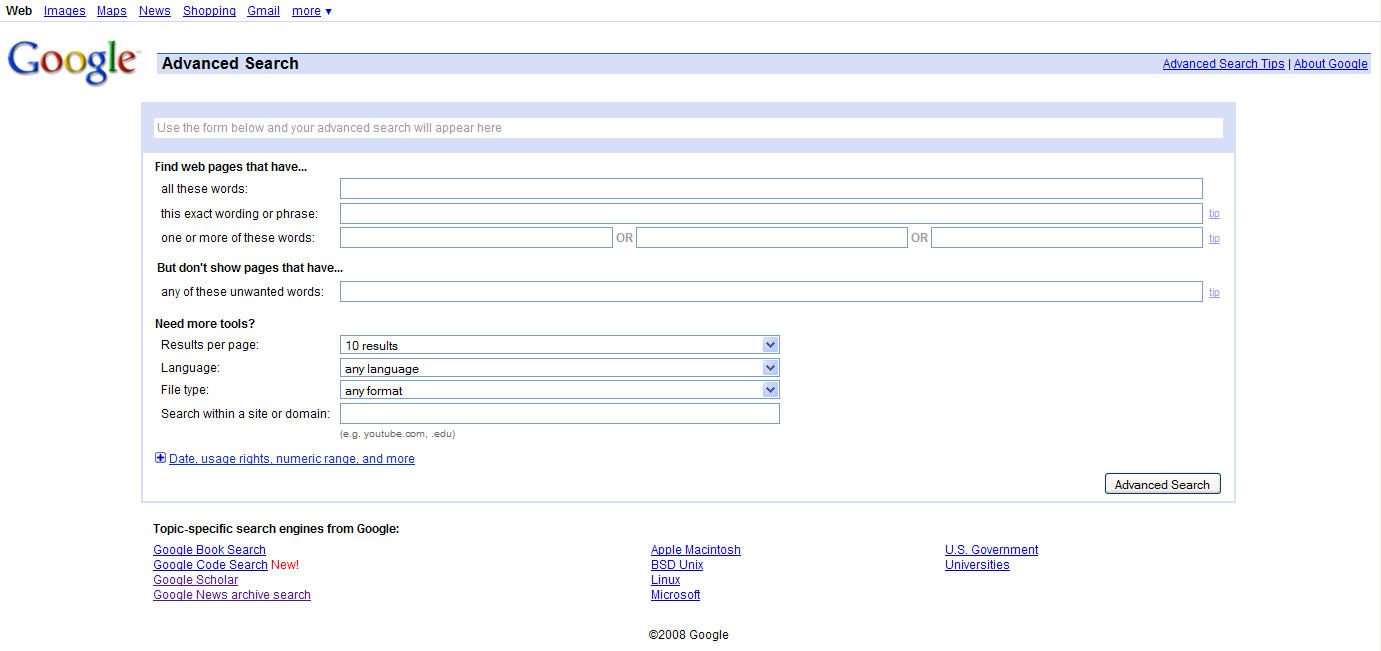
The good effect of these changes quickly became clear. The number of users that bounced out of the Advanced Search page dropped significantly. Interestingly, the total number of Advanced Search page users didn't increase significantly... at least not yet. By improving the UI on the page, we hope to attract even more searchers to the large range of search options available on Google.
In the end, this example shows the kind of insights that field studies can bring. As with the eye-tracking example, asking someone about their emotional response to a web page just isn't a useful way to get that data. But watching them in situ, as they actually use Google to go about their daily search lives can reveal all kinds of remarkable, otherwise undiscoverable, and actionable insights into searcher behavior.
Daniel Russell, Uber Tech Lead, Search Quality
googleblog.blogspot.com
published @ November 7, 2008